-

Low Cost, Adhesion Strength Based Cell Sorter
Emily Burtch, Franck Kamga-Gninzeko, Devin Mair, and Sarah Saunders
In many in vitro experiments, primary cells are harvested from an animal species to undergo experimental manipulation and subsequent analysis. Cell sorters are a luxury to have after cell harvesting to ensure pure populations of cells. Recently, it was discovered that different cell types adhere to cell culture dishes at different strengths. This observation was utilized in the invention of a cell sorting system that sorts cells based on this adhesion strength difference. The resulting system is marketable at under $2000, compared to $50000 plus for current commercially available systems, and is the first commercially-oriented cell adhesion strength based cell sorter. The system allows for use of tissue culture flasks, a tool that any researcher using cells will be very familiar with, that have been customized with a removable bottom. After cells are adhered, the bottom is removed and placed into the cell sorting system and sealed with a removable sealing putty. Flow is imparted to the cells, generating a shear force over the surface of the cells, lifting the cells and depositing them into a centrifuge tube. Prior experiments have shown this system to have a cell purity and cell viability greater than currently available solutions without the use of expensive antibodies and using equipment available at a fraction of the cost.
-

Low Cost and Durable Perovskite Solar Cells
Jack Carli, Kapil Marahatta, Feras Kakish, and Jason McAleese
Perovskite solar cells offer an alternative approach to photovoltaic solar power generation versus traditional silicon solar cells, by rivaling their efficiency at potentially less than half the cost. Perovskite’s name comes from the crystal structure that encompasses the active layer (Methylammonium Lead Iodide – CH3NH3PbI3), the region that absorbs photons and generates electrical energy by creating electron hole pairs. The presence of the organic cation (methylammonium) causes degradation of the active layer under humidity, UV light, and high temperature, which lowers the effectiveness of the cells. This project investigates low-cost routes and materials for realization of high efficiency and long-term perovskite solar cells. In order to combat humidity, the device is encapsulated, usually with a polymer coating. Moreover, the UV photons, which otherwise would be filtered by the glass substrate are converted to visible photons by a photon conversion layer, which is coated on the opposite side of the substrate from the device itself. These visible photons can then reach the active layer and add to the electrical energy generation, enhancing the device efficiency. The low production cost of these solar cells originates from the low processing temperatures, under 150°C, compared to silicon, 1400°C, and simple fabrication procedures. Not only do the lower temperatures reduce cost, they also reduce the carbon footprint of the fabrication process. In addition, perovskite solar cells can be fabricated on light-weight and flexible substrates, widening the range of their potential applications, which include powering surveillance drones and wearable sensors implemented in the warfighter’s uniform.
-

VCU Pathfinder
Chris Carpenter, Christian Merk, and Syed Shahriyar
Imagine this, you are planning to enroll in an institution of higher learning. However, your schedule can't possibly match your institutions recommended path. Maybe you're transferring from a different institution, maybe you just picked up additional hours on the job, or maybe you just want to change to a different major. Getting all the information you need in one place to plan a personalized schedule can be a difficult proposition, especially if you don't have easy access to an on-site adviser. VCU Pathfinder is here to make this process considerably less stressful and more efficient. Pathfinder is a schedule assistance tool available through a web browser. All the information that a student needs to know in regard to planning their schedule, such as degree requirements, course prerequisites, credit amount, and individual semester availability of courses, is handled by the website. By utilizing an intuitive and flexible interface that color codes courses according to what a student can take according to the degree they've chosen, Pathfinder answers the question of "Can I take this course at this date?". It's as simple as that. There's no need to dive through bulletins to understand your course flow or when courses are available. All the information used by the service is maintained in a Maria database that can be easily edited by an adviser with no prior programming experience.
-

AMC Native WebRTC Client
Kellan Childers, Michael Dowling, and Sherdil Khawaja
Traditional call center and telecommunication hardware is being replaced by thin, browser-based, cloud enabled web services. Industry standards for web based communication protocols, such as WebRTC, are being established. AMC needed to address this new technology, while maintaining a hybrid approach of server-based capabilities, taking advantage of the web-based communication channel, while broadcasting events to the Contact Canvas Server. Contact Canvas Agent Palette is the editing platform of the AMC adapter for Salesforce.com, allowing agents to communicate with customers through the AMC adapter/ Softphone. Using Agent Palette, the task was to integrate Video Chat using WebRTC into the AMC toolbar. Two agents use a peer-to-peer connection to establish communication with one another. The connected two can communicate through video chat which supports screen pop. The components that were provided and used were the AMC adapter for salesforce.com, the Agent Palette, and the salesforce.com Customer Relation Management (CRM) database. The AMC adapter is an HTML Softphone that can be used to voice enable salesforce.com, while Socket.io and Node.js were used to communicate with the server side. Eventually this video chat will advance to the point where communication will be established between agents and their customers.
-

Smart Exoskeleton Hand with Soft Electronics
Andrew Choi, Han Ha, Gabrielle Jones, and Gregory Zobel
Many people in the modern world suffer from a loss of hand and finger strength due to diseases in the muscle or nervous system such as ALS, Muscular Atrophy, and more. This problem has become more widespread with the surge of technology over the last 5-10 years. Therefore, we have created a smart exoskeleton hand with soft electronics that will allow people with less than average hand strength to perform daily activities.
The exoskeleton device utilizes small, lightweight linear actuators to provide additional strength to the user’s fingers and the hand itself will be 3D-printed with ABS and PLA plastics to allow for a lower cost while maintaining the strength requirements. The smart exoskeleton also contains a feedback system that processes electromyogram (EMG) signals through a custom circuit in order to replicate the real time movement of the user. These signals are then saved as a data file and stored to allow physicians to analyze these signals and find trends of either reconstruction or deconstruction. This system is powered by two AA batteries and one 6V battery housed in a custom, 3D-printed battery pack. A small touch LCD screen has been installed to display the filtered signals from the EMG sensors attached to the users arm while also showing the current battery life of the device. All of these components incorporated into one system allow for a lightweight, portable design that provides the user with the ease of normal mobility.
-

Media Mixing Apparatus
Nick Colt, Eric Depew, Kurt Thoele, and Chris Ward
The purpose of this project is to reduce the physical exertion and radiological exposure of the maintenance worker by reducing mixing time of water and resin beads when replacing resin beads in a shipboard tank. Presently, a maintenance worker empties ⅓ cubic foot of resin media into a bucket, and fills the bucket with about 1-⅓ gallons of water. Then the water and resin media is mixed with a paddle by hand, until it appears homogeneous, creating a slurry. The slurry is dumped into a funnel after the mixing process and introduced to the system after the discharge valve is opened. This process is ineffective, as the water and resin tend to separate before the funnel empties. The introduction of a mixing apparatus will increase the efficiency of the mixing process and thereby decrease the time necessary to create and maintain the homogeneous slurry prior to discharge into the onboard tank. This method will reduce worker fatigue, worker radiation exposure, and the overall time lost to constant remixing due to settling. The design will be easy to replicate and redesigned if necessary to fit alternate funnels. The construction of the mixing apparatus will require relatively inexpensive components and can be completed in a short amount of time, adding to the overall efficiency of the design.
-

Portable Pure-Tone Audiometer
Zachary Conner, Zachary Clute, Min Su Ju, and James Le
This project addresses the issue of making hearing tests available to more people, specifically those who live in parts of the world where audiologist are not readily available. Most countries around the world, including first-world countries, have a large gap in hearing testing when put in the perspective of the amount of hearing loss in their people. Most portable audiometers only perform air conduction hearing tests, yet physicians are in need of vital bone conduction information for proper diagnosis. To address this need, we developed an audiometer that is portable, yet also supports air and bone conduction testing. Features that allow portability include noise cancelling headphones, battery power, and a small form factor. With the inclusion of noise cancelling technology, this device eliminates the need for a sound-proof booth to perform hearing tests. Additionally, an audiologist is not required to perform the hearing test due to the automated test procedure and intuitive user interface. With this feature set, this device will be portable enough to be used by screening organizations in third world countries while still providing sophisticated diagnostic information normally only available in audiology clinics.
-

StackInTheFlow: StackOverflow Search Engine
John Coogle, Jeet Gajjar, and Chase Greco
Programmers increasing rely on an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), which offers capabilities for writing, debugging and testing code. Most developers, ranging from novices to pros, reference outside sources when developing, such as the popular Q&A site StackOverflow. In the 2016 StackOverflow Developer Survey it was observed that 78% of survey participants visited StackOverflow at least once a day, with 58% visiting multiple times a day. The purpose of the StackInTheFlow software development tool is to reduce the amount of time and interruption necessary to gather external information during development. This enables the developer to remain in-the-flow of solving software engineering problems. This tool not only provides standard information retrieval capabilities similar to popular search engines such as Google, but also a feature to auto-generate queries based on the developer’s current work context, extracted from within the IDE. The auto-query feature functions by first extracting features from the IDE, including snippets of source code such as import statements and the current cursor line, as well as, if available, compilation error messages. From these features candidate query terms are extracted. These candidate terms are then compared against a dictionary constructed from a dump of all StackOverflow articles. From this dictionary, various retrieval statistics for pre-retrieval query quality are computed for each term. The highest ranking terms are then chosen to form a query which is sent to the StackOverflow API and the relevant questions are returned and displayed to the developer.
-

Finite Element Analysis of a Friction Clutch System in an Automatic Transmission
Samuel Cook
The purpose of this project is to develop a computational solution to the effects of certain variables present inside an automatic transmission, more specifically, the friction clutch system that enables and disables different gear-sets. Afton partnered with the School of Engineering looking for a time-sensitive, computational solution to serve as a valuable comparison to what exists at Afton’s disposal currently. The solution is a finite element analysis (FEA) simulation that transforms a real world device with many nuances and intricacies into a simplified model in a two dimensional test space. The challenge exists in keeping the simplified model accurate to the real world system. With this in mind, a solution has been made that generates consistent results that match the theory behind fluid mechanics principles. With a working simulation made, certain variables such as plate structure and rotational speed have been able to be tested to show their effect on the amount of torque generated by an actual clutch system. This solution validates the decision of Afton to choose a simple alternative to conducting their own tests if they wish to do so.
-

PicShare
Kyle Crane, Emily Klein, and Ben Wunschel
PicShare is an app that allows companies to easily manage their social media presence without having to dedicate large amounts of time to the process. Your social media department can now extend their reach with the help of all of your other employees.
Our platform allows users to upload images/text from a mobile application or directly from the web. Administrators have the ability to take their own or user's image/text uploads and prepare for a social media post.
Employees attending events can get content to your social media staff much faster and with more variety. Our application is a great way to get your staff involved in spreading the word about your company. At the same time, you can maintain the security of your social media accounts by only entrusting credentials to administrators.
We have created a one stop shop for social media staff to work from because we allow for connection of multiple accounts. Customers working as administrators within our application can post to multiple social media accounts and multiple accounts within each of our connected platforms.
-

Design and Prototype of Next Generation NASCAR Brake Caliper
Jesse Crowder, John Knighton, Lenny Ports, and Miranda Snyder
Efficient braking is pivotal to the success of a NASCAR team. Braking occurs when the brake pedal is depressed, causing hydraulic pressure within the caliper housing and on the pistons, which forces the pistons to push the brake pads against the rotors reducing the vehicle’s speed due to the high friction between the pads and rotors. High performance brake calipers are arguably one of the most crucial components of a race car braking system. Short track brake calipers were designed to efficiently decelerate vehicles traveling upwards of one-hundred twenty miles per hour. This is an essential function of vehicles on short tracks due to their characteristically short straightaways and tight turns. Therefore, the objective of this project was to reverse engineer a brake caliper capable of competitive performance under the extreme conditions of short track racing, while simultaneously reducing the weight of the caliper and maintaining its structural integrity. The reverse engineering process was accomplished by scanning the brake caliper in VX Elements, using the scanned data to create contour geometry in SolidWorks, which was then used to effectively model and prototype the brake caliper. To ensure structural integrity, strain gauge testing, material testing, and a finite element analysis were performed. This testing was used to validate the model and justify structural modifications for weight reduction. Reducing the weight of the brake caliper will give the NASCAR team a competitive advantage in short track racing.
-
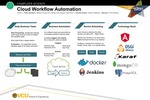
Cloud Workflow Automation
William Crump, Eric Darling, Kyle Hagood, and Syed Rizvi
The goal of our project was to develop an application in the cloud which automates complex business tasks. The application allows users to create configurable events consisting of a trigger followed by an action. Triggers are designed for common tasks such as scanning a directory or email inbox for new files. When a new file is detected, the application triggers the execution of an associated action such as sending an email alerting the user of the changes or processing and moving the files. Users are thus able to automate complex tasks by configuring event sequences, leading to an increase in productivity and work efficiency on a daily basis.
The project also investigated the logistics of deploying applications to the cloud, by researching new tools and technologies used for cloud deployment. Our project consists of a REST driven server, along with a website and a small desktop tray application. We successfully employed several technologies for continuous integration and modular design. Also by hosting the application as a service in the cloud, we solved several problems for both the customer and the applications’ developers. There is no need for a lengthy installation process for the customer, and the developers now have an easier way to regularly update the application to meet customers’ needs. The outcome of the project was both a developed cloud application and research on new technologies for cloud deployment.
-

Lab-scale Reproduction of Siloxane Foam Synthesis
Albert DeAngelis, Benjamin LeDoux, and Conrad Roos
Evonik has a synthesis reaction to create siloxane-based foam for sale that they run in their Hopewell plant. They would like to utilize a bench scale reactor system for experimentation on the process. The problem is that the foam created on the lab scale does not show the same properties as the foam created on the plant scale and to run experiments accurately they would have to use the plant reactor, wasting both reactor time and plant resources. Evonik wanted the Senior Design team to find a way of recreating the conditions of the plant reactor on the lab scale so that experiments could be run in a way that eliminates waste and gives accurate data.
The final direction of the project was to provide a 1 Liter jacketed glass reactor and an outline for a recirculation bath that would mimic the heating profile of the plant reactor as closely as possible, as well as a way to provide a comparable agitation profile to the plant scale. To facilitate the agitation profile, an equation was found to relate the size and speed of both the lab and plant impellers. In addition, a quantitative method of measuring “good” and “bad” quality of the product was discovered in UV-Vis Spectroscopy, which allows Evonik to instantly test the liquid product without having to “foam up” the product and test qualitatively.
-

S.H.I.E.L.D Relays (Shadow-masked Hack-proof Ion Etched Latch Deterrence Relays)
Anh Dinh, Adrienne Ilustre, Thomas Nuckols, and Sean Payne
We are presenting micro-scale logic devices using single cantilever relays fabricated in-plane from single crystal Silicon. These logic devices are designed to protect electrical systems that require a high level of security by being completely hack proof by not having the ability or need to be connected to any outside internet connection. Because these devices are fabricated from silicon, they are extremely reliable, durable and adaptable. Silicon’s high Young’s Modulus allows the cantilevers to function for an extremely long time, compared to other materials such as metal that will start to fatigue over time, producing a longer life span of the devices. The logic devices are also Rad-Hard and chemically resilient. This allows the devices to remain durable in many types of environments from satellites orbiting the Earth to Nuclear power plants and submarines to industrial manufacturing plants with harsh chemicals. These devices can also be fabricated to have device actuation voltages from a fraction of a volt to tens of thousands of volts allowing the devices the ability to function in almost any electrical system.
We have also innovated a new processing procedure using hi-resolution shadowing masking techniques that improves the fabrication of these devices. By using the hi-resolution shadow mask, we are able to reduce the number of steps required to fabricate the logic devices, shorten the processing time and reduce the chemical waste from fabrication. This allows the devices to be fabricated at a lower cost while also reducing the environmental impact from chemical waste.
-

Underwater Ant House
Mark Duggan, Zachary Ellis, and Zachary Soulier
The project seeks to design and test and submersible enclosure capable of sustaining oxygen breathing life. A mesh covered in a superhydrophobic coating can both restrain water up to a maximum pressure and retain a direct interface between air and water. Oxygen can transfer over this boundary if there is a sufficient difference in concentrations between the water and air.
Multiple designs have been produced with the intent of testing and demonstrating these theories. 3D printing allowed for quick and customizable production of every component. Enclosures were made for testing the maximum allowable pressure and to fit an oxygen sensor. These mostly consisted of a rectangular frame with slotted to fit removable mesh slides. Oxygen concentration experiments were conducted with crickets as live subjects and were designed to analyze the transfer of oxygen through the mesh. The team ran tests to investigate additional factors including coating application and quality, the influence of the mesh substrate material on hydrophobic and coating properties, and mesh sizing influence.
Testing indicates that there is sufficient oxygen transfer for small animals to survive. The enclosure can be submerged to approximately four centimeters before failure. This project demonstrates the feasibility of maintaining breathable air using a hydrophobic mesh enclosure and creates the opportunity for further investigation into possible uses of this technology.
-

Wearable Device to Detect Cardiac Arrest
Jon Dyke, Majid Alashari, and Ashraf Al Gumaei
Cardiac arrest is one of the leading causes of death globally and is unwitnessed in most cases. This begs the question: how can anyone know that an individual is experiencing cardiac arrest if no one is around to see it? MULT 603 has designed a cardiac arrest monitoring device that a person can wear on their wrist. This device detects the individual’s heartbeat; in the case that the person’s heartbeat drops below their normal individual threshold, their family, doctors, and friends along with emergency medical services will be notified of their location and condition. The hope is to drastically improve response times, put the minds of families in which a loved one has had past heart complications at ease, and eliminate unnecessary loss of life.
The branding for this concept is named Cardian, a hybrid of “Cardiac” and “Guardian”. The mission of Cardian is to provide ease of mind and eliminate unnecessary loss of life by utilizing simple and easy to use technology and pairing it with powerful engineering and emergency medical services. The primary customer (the target market) is those age 65 plus with heart disease. The unmet need is a gap in telehealth services (NAICS 621999) for autonomous alerting of medical emergencies; in this project, the emergency of SOHCA. Over 85 million Americans have some form of heart disease, and the target market makes up of 40 million of this number. At one percent market capture and the current price point of $150, annual revenue potential is $60,000,000.
-

Infrared Stereo-Vision Target Tracking Robot
Alex Elliott
Computer stereo-vision consists on a system that is able to obtain, estimate, and extract distance information of a scene in space from a set of 2D images. The system can be upgraded one step further by utilizing LWIR (Long Wave Infrared) sensors, in order to potentially place the system in low-visibility scenarios where ordinary color sensors might not be the best option. The data streams via an analog signal and is converted to serial-USB to be processed. The sensors are placed parallel, mounted on a bracket and attached to a robotics platform.
In order to estimate depth, a concept called stereoscopic vision is implemented similarly as humans perceive depth. If two sensors are placed into a scene, Epipolar Geometry can be used to obtain distance by calculating the disparity (distance) between matching feature points. The feature points are matched based on the cost from a SAD (Sum of Absolute Differences) algorithm. This algorithm finds a block of pixels from the reference image (Left) and calculates the SAD based on pixel intensities on the target image (Right). This search is simplified by rectifying the two images. This means that each possible feature point is located along the same pixel row, eliminating the need to search vertically. The block with the smallest cost along each pixel row is considered to be the best match. This disparity is inversely proportional to the actual distance of the object (human) and is then sent to the robot in order to track.
-

C.A.R.E (Cohort Assessment & Retrieval Environment)
Kyle Ellis, Payal Shah, and Jordan Tang
The purpose of clinical trials is to explore whether a medical treatment is safe and effective for humans or to enhance preexisting methods. The identification of patients who satisfy a set of predefined criteria for the trial is instrumental. However, the process of distinguishing these patients on the basis of their clinical records is a challenging task since it can have structured (ex: precise measurements) and unstructured data (ex: physician notes). One difficulty with this is data normalization; there are many ways to describe a single concept. For example, “heart attack” and “myocardial infarction” both refer to the death of the heart muscle. The goal of this project is to develop a system that will process clinical records for the purpose of cohort discovery and make a visual framework to allow researchers to view and explore the associations between biomedical terms and their characteristics.
Steps: 1) The user inputs criteria on what they want/do not want in their patients’ medical records. 2) The criteria and patient records run through a system using MetaMap and MetaMap- DataStructures that measures the association between biomedical terms and links other terms to that word or phrase. 3) The patient records are ranked based on the user input criteria. Therefore, the records that have more prevalent information regarding the input criteria receive a higher score. 4) The user is able to see the records in the order they were ranked. This makes the process of finding patients for a clinical trial more manageable.
-

3D Printed Embedded Force Sensors
Derek Faltz, Chad Majewski, Andrew Perkins, and Faiwei Zhang
Additive Manufacturing and 3D printing has opened the door to an endless amount of opportunities, including recent advances in conductive and resistive circuit printing. Taking advantage of these new technologies, we have designed a 3D printed insole with embedded plantar pressure sensor arrays. The customizable aspect of 3D printing allowed us to uniquely design a multitude of sensors. With the use of a dual extrusion printer we were able to produce a model that printed both the resistive circuit and complete insole simultaneously. These distinctive technologies have given us the capability to capture valuable pressure data from the sole of the foot. Analog signals sent from the pressure sensor arrays are received and processed through an attached multiplexer designed specifically for this application. The signal is then digitized and transmitted over the SPI transfer protocol to a processor and wirelessly communicated, via Bluetooth Low Energy, to a mobile android device to allow the user to easily record and interpret the array's pressure data in real-time. The android device houses a pressure mapping view to show the gradient of force throughout the insole. With the capabilities of this insole we have provided an avenue for physicians and physical therapists to gather quantifiable insight into their patient's progression throughout the rehabilitation process. With more intelligent and personalized data the applications of this technology are countless.
-
Compressible Media for Water Treatment
Christine Forkins, Steven Kammermeier, and Antonio Musso
Tertiary water treatment is used to remove total suspended solids (TSS) from wastewater. Suez uses compressible media for their tertiary water treatment. There have been supplier issues in the past such as unreliability, long lead-times, unknown manufacturing process, and chances of resale. The chance of resale is an important issue because the specifications may change from one supplier to another.
The group was tasked to characterize different types of compressible media for water treatment, design a lab scale filtration unit, and design and manufacture a new media to be tested. In order to gain an operational expenditure advantage, Suez accomplishes media compression without the use of a mechanical device, which was taken into account when designing the filtration unit.
The media characterization determined that the media’s fiber was crimped polyethylene terephthalate and the node was atactic polystyrene. The original media was tested on the lab scale filtration unit at concentrations of 10, 30, and 50 mg TSS/L. Due to the size of PVC column diameter (3 inches), channeling and wall-effects were observed, which allowed solids to pass through the media. Because of these effects, the 10 mg TSS/L run was the only acceptable test in terms of turbidity requirements (<2 >NTU).
New media was designed and manufactured using uncrimped polyethylene terephthalate and hot melt adhesive. The team has future plans to test the new media on the filtration unit. It is expected that the media will be less successful because the fibers are uncrimped.
-

Automatic Parking Application
Corey Gates, Huy Nguyen, and John Steiner
The purpose of this utility application is to automatically remind the users where their vehicle is parked. Using many sensors and features of the Apple iPhone, we can track changes in users’ behaviors and their surrounding such as air pressure, physical movement, connection proximity, and coordinate position. These allow for detecting not just the parking position, but also altitude and interior approximation within parking structures. Using a periodic assessment loop, this application silently waits for changes, remaining out of sight of common user activity. During an assessment, nearby connections, user position, and activity readings are evaluated. If a significant event, such as getting in a car or driving into a known parking location occurs, relevant methods are initiated, allowing for greater accuracy and ultimately a better user experience.
Anyone who drives knows the struggle of searching for a parking spot for their vehicle. Finding the location of your parked car could even be more stressful. You may end up with walking up and down the stairs of a parking garage, wandering through a shopping center lot, or walking several blocks in the street only to remember the location of your car. Even once the car is located, it may be covered in tickets or impounded because of parking regulations. This scenario is especially true when users find themselves in a new city or in an unfamiliar part of the town. This application offers solutions to all of the cases mentioned above. An overview map displays nearby locations. Parking meters can be started to estimate fees and trigger alerts when time is low. When hunting for the tracked vehicle, directions can be requested through the application.
Currently this application demonstrates the algorithms necessary to track a user’s vehicle through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connection proximity. Utilizing Apple’s monitored regions, locations of interest allow for significant awareness by waking the application and performing relevant readings. Indoor position is determined using altitude readings, position plots, and headings with known location schematics. Users can save their personal locations and access features such as the building rendering, parking meter, and guided directions. A possible industry implementation of this application is the monitoring of businesses’ lots, allowing parking demand prediction along with restricting availability.
-

Reducing Noise in Automatic Transmission
Connor Golden-Weathers, Riley Hall, Matthew Bosco, and Felix Pyatigorskiy
The efficiency of an automobile increases as its running torque increases. This is an avenue for improving fuel economy that is actively being pursued. However, transmissions running at higher torques produce an unacceptable amount of noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH). NVH occurs most visibly as a result of the vehicle’s friction clutch behavior. At present, machines capable of testing this behavior exist (MTM machine and LVFA rig) but are very expensive in terms of time, space, and production cost.
The goal of this project is to produce a cost-effective machine in which friction clutch behavior can be analyzed in a laboratory setting. Due to the complex nature of this project, multiple teams will be working to refine and improve the instrument over time. The first iteration of the machine produced by a previous design team was very limited in its ability to produce data efficiently. This design team took on the challenge of automating data collection for the load cell and thermocouple installed by the previous team, as well as implementing automated instrumentation capable of measuring motor torque and speed.
The new instrumentation of the machine is illustrated below, with the measurements of torque, load, speed, and temperature being collected by an analog data acquisition system. The machine is now capable of simultaneously recording these values, producing results such as the graph shown below. In addition to the sensor additions, the team made structural modifications to the machine to accommodate the torque sensor assembly.
-

Rapid, Diagnostic Test for Cardiac Ischemia
Jose Gonzales, Abdelmagid Nasreldeen, Emerson Physioc, Julio Contreras, and Evan Thoresen
Current methods to detect cardiac ischemia rely on biomarkers such as troponin. Elevated levels of troponin are observed hours after the cardiac event. There is an unmet need for rapid diagnostic tests for cardiac ischemia, which utilizes recently discovered biomarkers. A VCU patented assay for cardiac ischemia employs the use of chemiluminescence to detect metabolic byproducts of xanthine oxidase activity. These byproducts are detectable minutes after the cardiac event. Early diagnosis of and response to cardiac events is beneficial for clinical decision-making; therefore, a point-of-care device within the emergency health setting is sought. The CLSE 203 project team designed and fabricated a multi-layered lab-on-chip to not only house this rapid assay to be later implemented into a point-of-care device, but also convert the assay from a multi-step to a one-step process. The topmost layer contains the necessary reagents and blood plasma and introduces them into the assay. The middle layer passively mixes the reagents and the plasma together via a micromixing channel and introduces them into an Archimedean clockwise spiral. At the end of this spiral, the combined reagents sink to the bottom layer into a complimentary counterclockwise spiral and ultimately exit through a side of the chip. The two spirals form the area of detection, a complete circle. Metabolic xanthine oxidase byproducts are then detected and measured.
-

Assistant Suite
Dale Greene, John Pham, and Ritvik Nag
This project was conducted to demonstrate a voice-to-mechanical application from one source to multiple platforms with the use of hardware-to-software technology. The main platforms that are used for implementation is an Amazon Echo Dot, which serves as the voice interceptor to transcribe speech through integrated software hosted within the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud network, and a Raspberry Pi microcontroller, which serves as the device which controlled mechanical movements based on what is transcribed from the Echo. The user can speak a command into the Echo to control the movement of one of two RC cars without any physical engagement. The Echo utilizes Wi-Fi to connect to the AWS cloud network to transcribe the speech, which then goes through a series of channels to communicate with a microcontroller that is connected to its own RC car to cause that selected RC car to move in a specified direction. For example, the user can speak a command that says “Alexa, move car A forward for two seconds,” and this will translate to the selected car to motion forward for a total of two seconds. The project also displays the usefulness of being able to speak to multiple microcontrollers connected to separate devices under a single application; this caters to the convenience of not having to close and open separate applications every time a different connection is needed.
-

Development of a Tabletop Soft Gel Encapsulation Machine
Brigitte Ha, Emily Miller, and Haya Rizvi
Currently, to test new formulations of gel capsules at Pfizer, they must use the large-scale machine that requires a minimum of 25 kg of gel melt and produce hundreds of capsules per run. Production at a smaller scale to enable rapid changeover for research and development is desired. The team’s goal was to achieve continuous production of sealed capsules with 80% fill capacity. Capsule sealing was the prime consideration. Preliminary trials using the existing system and heat transfer analysis indicated localized heating was necessary to promote capsule sealing. To provide localized heating, a brass wedge was designed based on the pilot scale machine. The machined wedge was integrated with a PID control system. Using pre-made gelatin ribbons, the appropriate process parameters to achieve sealed capsules were determined. The critical, coupled parameters were die roll temperature, wedge temperature, wedge height, and die roll speed. Capsule sealing efficiency was highest at a speed of 4 capsules/min. For air-filled capsules, a sealing efficiency of 100% was achieved. For PEG-400-filled capsules, a sealing efficiency of 50% was achieved. Future work will include integration with the gelatin feed system and addition of a vacuum during capsule formation to increase fill capacity.
The Capstone Design course at the College of Engineering of Virginia Commonwealth University is meant to be the climax of every engineering student’s undergraduate education. As a prerequisite to attaining a Bachelor’s degree, the Capstone Design course presents each student with the challenge of working in a team to tackle actual engineering problems within and across the fields of Chemical and Life Science, Mechanical and Nuclear, Biomedical, Electrical, and Computer Engineering and Science. At the end of the two semester course in April, the student teams present their work to the sponsors, faculty, students, invited guests and the general public at the Capstone Design Expo, held at the Virginia Science Center in Richmond.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.


